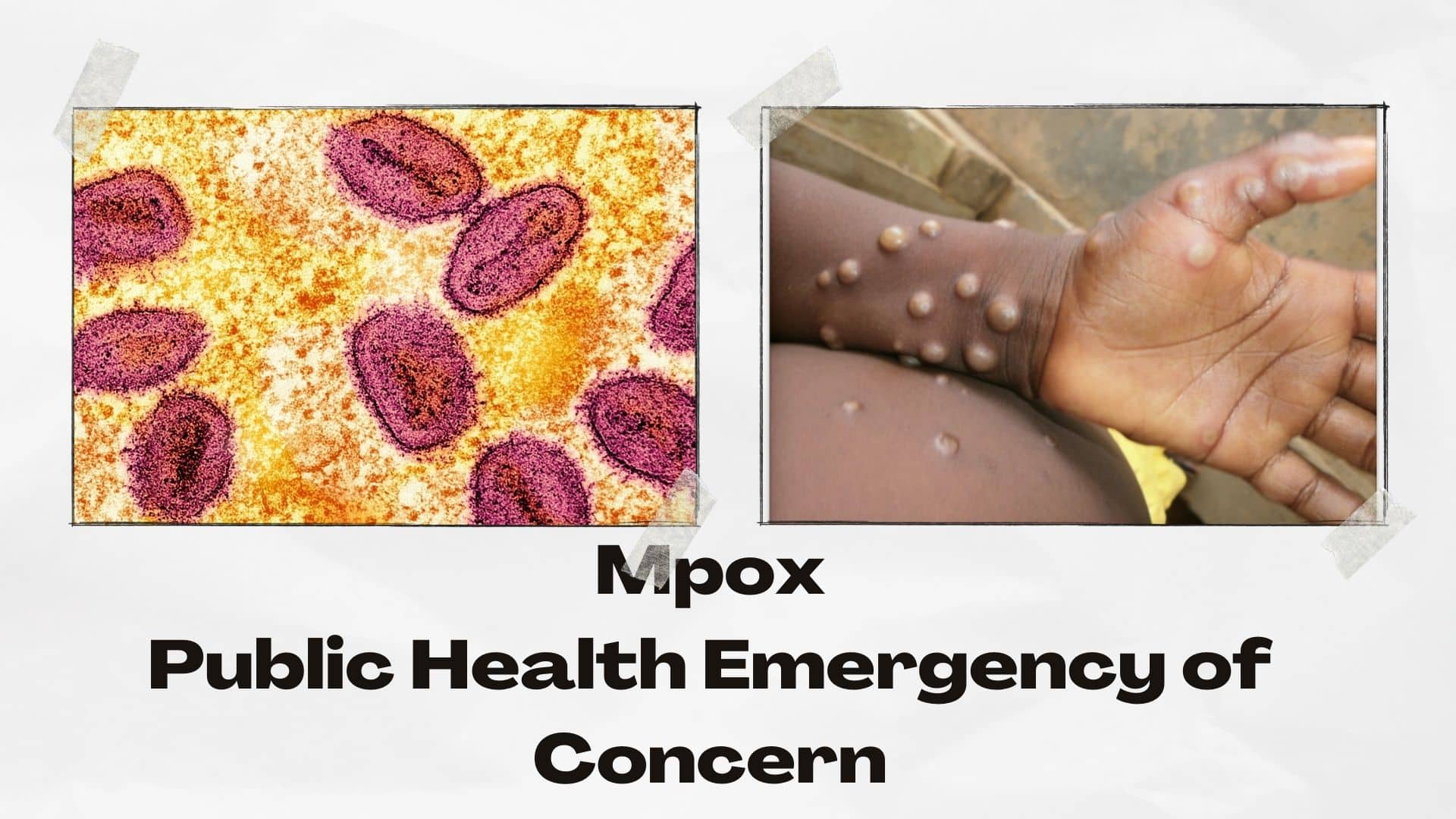
Mpox (formerly known as monkeypox) is a viral disease that has been around for many decades, but we are seeing a resurgence in cases in the past few years and in places where there was previously no transmission. The WHO has declared mpox to be a Public Health Emergency of International Concern due to ongoing human-human transmission, which has previously not been observed. It is not currently considered a pandemic. Australian healthcare authorities are actively monitoring the situation and there has been an increase in availability of the mpox vaccine which is now available (pending stock and demand) through GP clinics for specific populations.
Mpox is largely not an airborne virus and is mostly transmitted through close contact and bodily fluids. The disease is usually self-limiting and can last for 2-4 weeks. Commonly there can be a pox-like rash and while these are present, individuals remain contagious. Other symptoms can be general including but not limited to fevers, headaches, myalgia (muscle pain), back pain and sore throat.
There is a vaccination treament available which is highly effective against mpox and smallpox. It is a 2-dose vaccine given 4 weeks apart.
At time of writing, the mpox vaccine is available as Post-exposure Preventive Vaccination (high-risk exposure in the previous 14 days) or in the following groups as Primary Preventive Vaccination:
1) Men who have sex with men and their partners
2) Sex workers
3) Anyone at greater risk of a poor clinical outcome from Mpox infection e.g. immunocompromised individuals
4) Anyone with occupational risk e.g. laboratory staff handling mpox specimens; healthcare workers at higher risk of exposure to patients with mpox; sex-on-premises staff etc.
5) Travellers in the above groups to countries experiencing a significant outbreak
The mpox vaccine available is not a live vaccine, but is made from a modified virus similar to smallpox and monkeypox viruses. It does not cause disease in humans and is non-replicating (AIH). It is also effective against smallpox, which was a naturally occuring viral disease considered eliminated in the 1970s. Interestingly, the current vaccination is also effective against smallpox, a viral disease which was considered eradicated in the 1970s.
If you’re concerned about mpox, we suggest booking an appointment to discuss your concerns with a GP in the first instance. If there is concern regarding a rash or symptoms, please consider a more urgent review and notify reception prior. We love photos, so taking photos at different stages can help us further diagnose any issues.
https://fb.watch/vBYFH57pyC/